
Liabilities are classified as non-current based on their maturity date extending beyond one year from the balance sheet date. This distinction is crucial for understanding a company’s long-term financial strategy and its ability to sustain operations over time. It reflects the company’s financial structure, investment strategy, and the confidence of long-term creditors in the company’s future. Non-current liabilities provide insight into the company’s approach to leveraging debt for growth and expansion, highlighting its financial commitments and the timeline for meeting these obligations.
Current Liabilities
Creditors (people who lend money) and investors (people who buy parts of companies) can see how easily a company can turn its assets into cash to pay off debts. The classified balance sheet improves transparency by categorizing items and helps stakeholders assess liquidity, solvency, and overall financial health. By organizing financial data into clear categories, it offers deeper insights into liquidity, financial health, and the nature of assets and liabilities. The detailed categorization of your business’s assets and liabilities in a classified balance sheet will help anyone viewing your balance sheet easily access the specific information they need.
- Basically, this is the amount of principle needed to be repaid in the following year.
- These are short-term resources that are utilized within the operating period, usually a year.
- If several persons are involved in a business that is not incorporated, it is likely a partnership.
- Each category groups similar items, such as cash under current assets or long-term loans under non-current liabilities.
- The four remaining asset classifications contain assets that a business expects to hold for more than a year.
- A classified balance sheet should be prepared regularly, typically at the end of each accounting period (monthly, quarterly, or annually).
Example 1: Small Retail Business
- It lists its current assets (cash, accounts receivable, and inventory) totaling $500,000 and non-current assets (property, equipment, and goodwill) totaling $1,500,000.
- In addition to classifying assets and liabilities, equity is also presented on the balance sheet.
- An unclassified balance sheet presents a company’s financial data in a straightforward format.
- The purpose of the classified balance sheet is to facilitate the users of financial statements.
- While the classified balance sheet format provides more information than the unclassified format, some businesses prefer the latter because it is simpler and easier to understand.
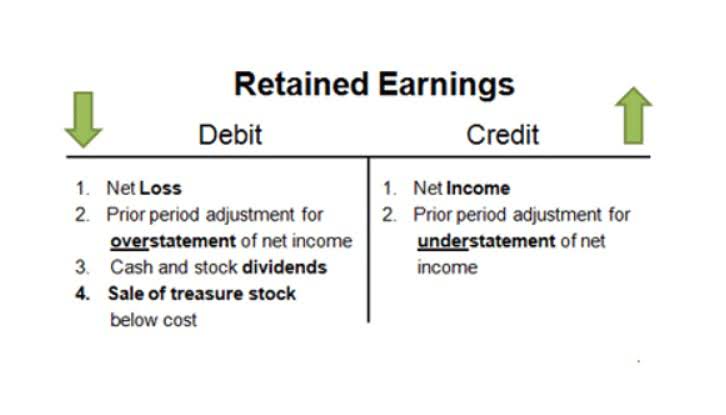
We have also examined how they serve as essential guides for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and internal management. Owner’s equity, known as shareholders’ equity for a corporation, is the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities, representing the ownership stake in the company. Its main components are common stock, which is capital invested by shareholders, and retained earnings. Retained earnings are the cumulative net income not distributed to shareholders as dividends. Assets are economic resources a company owns that are expected to provide future benefits. In a classified balance sheet, assets are separated into two categories based on when they classified balance sheet are expected to be converted into cash or used up.
Preparing a Classified Balance Sheet
Additionally, contingent liabilities, unless probable and measurable, and non-legal obligations or informal debts are typically excluded. A classified balance sheet organizes assets, liabilities, and equity into specific categories for clarity and detailed financial analysis. A classified balance sheet is a financial statement that reports the assets, liabilities and equity of a company. It breaks each account into smaller sub-categories to provide more value for the user of this report.
Classified Balance Sheet vs Unclassified Balance Sheet Examples
Understand how the organization of a balance sheet reveals a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations and support deeper financial analysis. Creating a classified balance sheet is like organizing your room into sections so you can find everything easily. This guide will show you how to sort a company’s assets, liabilities, and https://www.bookstime.com/ shareholders’ equity step by step.


Items on the balance sheet such as allowance for doubtful accounts and allowance for bad debt are based on estimates. If these estimates are incorrect, the QuickBooks net value of the asset can be under- or overstated. Each category is broken down further into specific line items, depending on the company’s business operations and accounting practices.
